|
|
User defined Ellipse Function in Python Canvas
使用者自定橢圓函數
By daych169
(1)
Introduction:
After
using Python canvas to draw widget shapes , I find out
(1) pure
python canvas cannot use’ floodfill ‘ method to fill a irregular region
surrounding by primitive shapes.(2)canvas can only save the shapes to
printer postscript file, which could not redraw again,(3)The methods
such as find_closest , find_enclosed , find_withtag, etc. hard to edit
or modify a primitive shape in canvas directly. These issues mentioned
above can implement easily in vb6. So I plan to solve it follow the
concepts similar to the programs I designed before. First, we need to
classify the canvas primitive to four basic types (a)line(lines),
(b)polygons,(c)texts,
(4) images. Here we will focus on line and polygon only. Classify circle
arc, open ellipse , polyline, spline and other non_closed shapes as
line, and closed shapes, such as ellipse ,circle ,rectangle ,triangle
,closed polygon ,closed spline as polygon. Because Python Canvas polygon
method can use optional attitudes ‘stipple ‘ to fill irregular region
with predefined stipple or pattern(xbm or XBM file), to fill colors on
any closed region ,using ’activefill’to show a color when mouse move
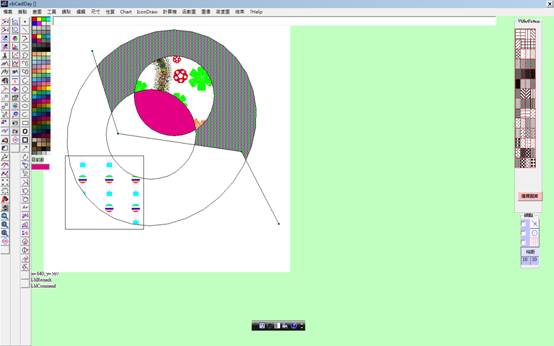
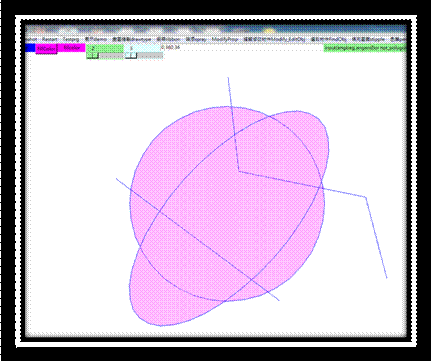
over the shape. Following are the shapes plotted by author’s progrm(vb
6).
 學習Python
tkinter canvas s畫圖後,發現(1)使用canvas在由兩 學習Python
tkinter canvas s畫圖後,發現(1)使用canvas在由兩
個圖元(primitive)以上所組成之不規則區域,無法直接在圖上使用洪溢填充方法(Floodfill,fill)鋪貼預設圖案、自定圖案或顏色,(2)
canvas畫完圖後想再行編輯及改變性質(edit primitive & modify
properties),所能使用之工具相當有限及困難,(3)canvas只能將圖元儲存成印表機認識之postscript
文字檔,似乎無法直接儲存成canvas相容之圖檔,需要時,能轉譯再繪成為原圖(redraw)。上述問題在vb6中實現並不困難,上圖就是我用vb6所設計之cad程式所繪製之圖案。因為有vb6之設計觀念,在研習多日後,終於研究出解決方法。利用tkinter
canvas所有提供之資源,實現解決方案。
Before introduce the user defined ellipse widget. I want to introduce
line draw method offer by Python tkinter(Tkinter) briefly. We are going
to implement the ellipse curve by canvas. create_line or canvas.
create_polygon method. The widget of python canvas supplies graphics
facilities for Tkinter(tkinter) .Among these graphical objects are
texts, lines, circles,polygons,ovals,arc,rectangle,windows, images, and
other widgets. With this widget it's possible to draw graphs and plots,
create primitive graphics editors, and implement various kinds of
user_defined widgets.
id = canvas.create_line(x0, y0, x1, y1, ..., xn, yn, option, ...)
The line goes through a series of points (x0,y0),
(x1, y1),
… (xn, yn).The
method create_line is used to draw a straight line or polyline. The
coordinates "coords"
are given as four integer numbers: (x0, y0, x1, y1 )for
a line ,and (x0,y0,x1,y1,x2,y2,x3,y3,….. ) for a polyline or smooth
curve_fitting polyline(set smooth=True) under the same name ‘line’. This
means that the line goes from the point (x0, y0) to the point (x1,y1, )
,and from (x0, y0) to (x1, y1) and then to (x2, y2)…….. for a polyline.
After these coordinates
follows a comma separated these list of additional optional parameters,
which may be empty or ‘None’. For example ,We can draw a line with
penwidth=3, color=’red’.This can be implemented something like
id=canvas.create_line(50,50,200,200,width=3,fill=’red’,arrow=None,activefill=’green’).
Here create_line is the method of
drawing by Python Tkiner, (50,50,200,200) is the coords ,width
is the keyword for pen size, fill is the
keyword of pen color, arrow is the keyword of
arrow of line(can be ‘tk.FIRST’,’tk.LAST’,’tk.BOTH’), and
actiivefill is the color of line when
cursor moving over the line, id is the return handler of line.
The options for polygon are quite similar to line, some useful
options,such as ‘stipple’,’outline’,’fill’are different with line.
‘fill’is used to fill the enclosed region,’outline’ is the color of
polygon boundary line,’stipple’ is the stipple or predefined pattern to
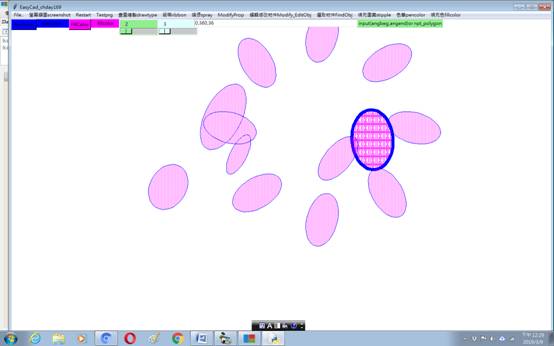
tile a closed region. The following diagrams are plotted by Arthur
designed python program. The irregular closed regional area are detected
first, and then it can be tiled with predefined stipple pattern or user_
defined pattern. Since the coordinates are found out, so the boundary
line length and area can be calculated as well. The algorithm of
detective method and xbp file making method and procedures are another
interesting issues, I would like to share friends in the future.

Python
tkinter自帶畫圖方法雖然可以繪製橢圓圖形,但只能畫垂直或水平,如要畫傾斜橢圓圖形,必須借用第三方提供之函數,如numpy,matplotlib等,
如要編輯或修改圖形相當不方便。本文所要討論的是,如何使用自訂函數繪製及編輯橢圓曲線。
(2)Governing equation of Ellipse and Ellipse arc:
The arc or oval methods offered by Python canvas can only draw the arc
or oval curves enclosed by a box. If you intend to draw an inclined
ellipse curve , You need to import numpy , matplotlib , PIL. ,
wxpython. Hereafetr, I like to discuss a user defined function to draw
ellipse by mouse or given three points to get an ellipse, simple and
easily. And you also can draw an ellipse rubber_band ellipse or ellipse
arc. The governing equation of ellipse curve can be defined like:
橢圓形曲線之方程式為:
(x-xc)**2/a**2 +(y-yc)/b**2=1
or
x=xc+a*cos(theta) y=yc+b*sin(theta)
通過平面上三個座標點可以定義一個傾斜之橢圓曲線。
Here (xc,yc) is the center of ellipse
a ,b is the semi diameter of long and short axis respectively.
If we give a three points(x0,y0),(x1,y1),(x2,y2) on a ellipse curve then
We can get :
xcen(xc)=(x0+x1)/2,
ycen(yc)=(y0+y1)/2
a= sqrt((x0 - xcen)**2 + (y0 - yeny) **2)
theta =atan2((y1-y0), (x1-x0))
b can be obtained after a, theta be solved.
def ellipse_Prop(x0,y0,x1,y1,x2,y2):
ptcenx=(x0+x1) / 2. # center of ellipse
ptceny=(y0+y1) / 2.
#print("ptcen.x,ptcen.y",ptcenx,ptceny)
angslop = math.degrees(math.atan2((y1-y0), (x1-x0)))
#print( 'angslop=',angslop)
aa = math.sqrt((x0 - ptcenx)**2 + (y0 - ptceny) **2)
#print('aa',aa)
ptanyx = x2
ptanyy = y2
#print('ptany=',ptany.x,ptany.y)
ta1 = ptanyx - ptcenx
ta2 = aa * math.cos(math.radians(angslop))
ta3 = -math.sin(math.radians(angslop))
#print('ta1,ta2,ta3',ta1,ta2,ta3)
tb1 = ptanyy - ptceny
tb2 = aa * math.sin(math.radians(angslop))
tb3 = math.cos(math.radians(angslop))
#print('tb1,tb2,tb3',tb1,tb2,tb3)
t1 = (ta1 * tb3 - tb1 * ta3) / (ta2 * tb3 - ta3 * tb2)
t2 = (ta2 * tb1 - tb2 * ta1) / (ta2 * tb3 - ta3 * tb2)
#print("t1,t2",t1,t2)
#print(1-t1**2)
bb=0
if (1.0-t1**2) >= 0.00001 :
bb = math.sqrt(t2**2 / (1.0 - t1 ** 2))
#print("bb",bb)
else:
print("error in function ellprop")
#print('aa,bb',aa,bb)
#xys=[ptcenx,ptceny,aa,bb,angslop]
#return xys #ptcenx,ptceny,aa,bb,angslop
return ptcenx,ptceny,aa,bb,angslop
#-----------------------------------------------------------------
def ellipsemaker_XY(x0,y0,x1,y1,x2,y2,angbeg,angend,npt,cenReturn=0):
# angbeg,angend are angles of ellipse beg. & end of curve
# npt are no. of point on ellipse
#
cenReturn=1, return (ptcenx,ptceny)
#print('x0,y0,x1,y1,x2,y2',x0,y0,x1,y1,x2,y2)
ptcenx=(x0+x1) / 2.
ptceny=(y0+y1) / 2.
#print("ptcen.x,ptcen.y",ptcen.x,ptcen.y)
angslop = math.degrees(math.atan2((y1-y0), (x1-x0)))
#print( 'angslop=',angslop)
aa = math.sqrt((x0 - ptcenx)**2 + (y0 - ptceny) **2)
#print('aa',aa)
ptanyx = x2
ptanyy = y2
#print('ptany=',ptany.x,ptany.y)
ta1 = ptanyx - ptcenx
ta2 = aa * math.cos(math.radians(angslop))
ta3 = -math.sin(math.radians(angslop))
tb1 = ptanyy - ptceny
tb2 = aa * math.sin(math.radians(angslop))
tb3 = math.cos(math.radians(angslop))
t1 = (ta1 * tb3 - tb1 * ta3) / (ta2 * tb3 - ta3 * tb2)
t2 = (ta2 * tb1 - tb2 * ta1) / (ta2 * tb3 - ta3 * tb2)
bb=aa
try:
if (1.0-t1**2) >= 0.0000001 :
bb = math.sqrt(t2**2 / (1.0 - t1 ** 2))
else:
#print("error in function ellprop")
pass
except:
pass
ndo=npt
ang0=angbeg
ang1=angend
if ang1 == 0.0 :
ang1= 359.999999
if ang1 < ang0 :
ang1 =ang1+360.0
angbeg=ang0
angend=ang1
delang = (angend-angbeg) / npt
xout=[]
yout=[]
pts=[]
for i in range(0,ndo):
angi = angbeg + delang * i
tpt1=aa* math.cos(math.radians(angi))*
math.cos(math.radians(angslop))
tpt2=- bb * math.sin(math.radians(angi)) *
math.sin(math.radians(angslop)) # 'xcoord(x座標)
ptsix=tpt1+tpt2
tpt3=aa* math.cos(math.radians(angi))*
math.sin(math.radians(angslop))
tpt4= bb * math.sin(math.radians(angi)) *
math.cos(math.radians(angslop)) # 'ycoord(y座標)
ptsiy=tpt3 +tpt4
ptsix=ptcenx+ptsix
ptsiy=ptceny+ptsiy
xout.append(ptsix)
yout.append(ptsiy)
pts += (ptsix,ptsiy)
#print("ptellp",i,ptellp[i].x,ptellp[i].y)
if cenReturn==0:
if abs(360-abs(angend-angbeg))<=0.01 :
xout.append(xout[0])
yout.append(yout[0])
pts +=(xout[0],yout[0])
return npt+1,xout,yout,pts
else:
return npt,xout,yout,pts
else:
if abs(360-abs(angend-angbeg))<=0.01 :
xout.append(xout[0])
yout.append(yout[0])
pts +=(xout[0],yout[0])
return npt+1,xout,yout,pts,ptcenx,ptceny
else:
return npt,xout,yout,pts,ptcenx,ptceny
#----------------------------------------------------
The ellipse drawing by python canvas like:
Canvas.create_oval(xmin,ymin,xmax,ymax)
is same as
x0,y0=xmin,(ymin+ymax)/2
x1,y1=xmax,(ymin+ymax)/2
x2,y2=(xmin+xmax)/2,ymax
xout,yout,pts=[],[],[]
ndo,xout,yout,pts=ellipsemaker_XY(x0,y0,x1,y1,x2,y2,0,360,36,0)
canvas.create_polygon(pts,width=2,fill='red')。
Function ellipsemaker_XY() can draw inclined ellipse also.
利用python canvas_create_oval(xmin,ymin,xmax,ymax)和自訂函數
ndo,xout,yout,pts=ellipsemaker_XY(x0,y0,x1,y1,x2,y2,0,360,36,0)
者相當,此處
xout,yout,pts=[],[],[]
x0,y0=xmin,(ymin+ymax)/2
x1,y1=xmax,(ymin+ymax)/2
x2,y2=(xmin+xmax)/2,ymax
但ellipsemaker_XY()可以繪製傾斜橢圓及橢圓弧。
---------------------------------------
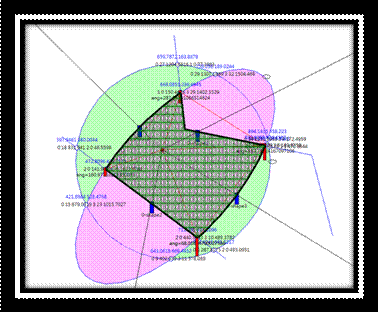
(3)Edit of ellipse :
The edit of ellipse curve such as rotation, reflection, offset ,
tangential line, copy(ring copy), segmental slice of ellipse by means of
python tkinter are difficult and complex ,but using user define
function are quite simple and easy. To fill or flood fill an irregular
region on PictureBox of vb 6 or vb net are simple and fast. But in
Python canvas shapes are difficult and tedious even on image。I
try to build a region passing through the boundary key points of the
interesting zone (surrounded by ellipse, or circle and lines) ,then fill
a predefined pattern or self defined pattern ) by python polygon
“stipple” and “fill”
method.(stipple=’hourglass’,stipple=’gray50,stipple=’@penginns.xbm’(user_definned
xbm file))。To implement this method, You need
to find out the segments of the connecting points, firstly. Here, I pose
some useful source code to get the ellipse segment to share with people
who is interesting.
Vb 6及net可以利用API函數直接在繪圖方塊(PictureBox)上不規則之封閉區域Floodfill及鋪貼圖案,但Python
canvas似乎並不直接支援此方法?好像只能在image上操作,因此本人嘗試計算不規則區域之邊界交點及曲線線段,然後與其他線段。理論上應該可行?

def EllipseReflct(x0,y0,x1,y1,x2,y2,angbeg,angend,npt,xbase0,ybase0
,xbase1,ybase1):
xout=[]
yout=[]
pts=[]
npt,xout,yout,pts,cenx,ceny=ellipsemaker_XY(x0,y0,x1,y1,x2,y2,angbeg,angend,npt,cenReturn=1)
xreflcts=[]
yreflcts=[]
for i in range(npt):
bol,xvert,yvert,xreftpt,yreftpt=NearPt_ReflctPt(xout[i],yout[i],xbase0,ybase0,xbase1,ybase1)
xreflcts.append(xreftpt)
yreflcts.append(yreftpt)
return npt,xreflcts,yreflcts

def EllipseRot(x0,y0,x1,y1,x2,y2,angbeg,angend,npt,xRotAt,yRotAt
,angRotIn):
xout=[]
yout=[]
pts=[]
npt,xout,yout,pts,cenx,ceny=ellipsemaker_XY(x0,y0,x1,y1,x2,y2,angbeg,angend,npt,cenReturn=1)
xrots=[]
yrots=[]
pts=[]
for i in range(npt):
xrtpt,yrtpt=RotatePoint(xout[i],yout[i],xRotAt,yRotAt,angRotIn)
xrots.append(xrtpt)
yrots.append(yrtpt)
xcenrot,ycenrot=RotatePoint(cenx,ceny,xRotAt,yRotAt,angRotIn)
return npt,xrots,yrots,xcenrot,ycenrot

def Offset_In_Out(x0,y0,x1,y1,x2,y2,angbeg,angend,npt,Offset,
isInsideOff=True ):
#print('in offset')
#x0=self.x0
#y0=self.y0
#x1=self.x1
#y1=self.y1
xcen,ycen,aa,bb,angslop=ellipse_Prop(x0,y0,x1,y1,x2,y2)
print('aa,bb',aa,bb)
xvert,yvert=ellPoint_byGivenAngle(x0,y0,x1,y1,x2,y2,90)
print('xvert,yvert',xvert,yvert)
ll=math.sqrt((xvert-xcen)**2+(yvert-ycen)**2)
raa=aa
rbb=bb
if isInsideOff==True :
ratpt=(aa-Offset)
rbtpt=(bb-Offset)
x0new=xcen+(x0-xcen)*ratpt/raa
y0new=ycen+(y0-ycen)*ratpt/raa
x1new=xcen+(x1-xcen)*ratpt/raa
y1new=ycen+(y1-ycen)*ratpt/raa
x2new=xcen+(xvert-xcen) *rbtpt/rbb
y2new=ycen+(yvert-ycen) *rbtpt/rbb
else:
ratpt=(aa+Offset)
rbtpt=(bb+Offset)
x0new=xcen+(x0-xcen)*ratpt/raa
y0new=ycen+(y0-ycen)*ratpt/raa
x1new=xcen+(x1-xcen)*ratpt/raa
y1new=ycen+(y1-ycen)*ratpt/raa
x2new=xcen+(xvert-xcen) *rbtpt/rbb
y2new=ycen+(yvert-ycen) *rbtpt/rbb
xoffsets=[]
yoffsets=[]
pts=[]
npt,xoffsets,yoffsets,pts=ellipsemaker_XY(x0new,y0new,x1new,y1new,x2new,y2new,angbeg,angend,npt,0)
#xoffset,yoffset=Ellip.Ellipse()
#print('xoffsets',xoffsets)
#print('yffsets',yoffsets)
return npt,xoffsets,yoffsets

def Ellipse2Tans(x0,y0,x1,y1,x2,y2,PtGivenX,PtGivenY):
EllpCenX,EllpCenY,AA,BB,angslop=ellipse_Prop(x0,y0,x1,y1,x2,y2)
ptAns1X = 99999.0
ptAns1Y = 99999.0
ptAns2X = 99999.0
ptAns2Y = 99999.0
Angslop=math.radians(angslop)
Ta = AA ** 2 * math.sin(Angslop ) **2 + BB ** 2 * math.cos(Angslop )
** 2
Tb = AA ** 2 * math.cos(Angslop ) ** 2 + BB ** 2 * math.sin(Angslop)
** 2
Tc = 2 * math.sin(Angslop ) * math.cos(Angslop) * (BB** 2 - AA ** 2)
Td = AA **2 * BB **2
Te = EllpCenX - PtGivenX
Tf = EllpCenY - PtGivenY
T1 = 2.0 * Ta * Te + Tc * Tf
T2 = Tc * Te + 2.0 * Tb * Tf
T3 = -(Tb * T1 - Tc * T2) / Ta / T1
T4 = 2 * Tc * Td / Ta / T1
T5 = Td / Ta
T6 = -T2 / T1
T7 = -2.0 * Td / T1
Fa = T6 ** 2 - T3
Fb = 2 * T6 * T7 - T4
Fc = T7 ** 2 - T5
tpt = Fb ** 2 - 4.0 * Fa * Fc
print('tpt=',tpt)
if tpt <= 0.0 :
print('no solution for Ellipse Tangent line')
return 'no solution'
else:
ptAns1Y = (-Fb - math.sqrt(tpt)) / 2.0 / Fa
ptAns2Y = (-Fb + math.sqrt(tpt)) / 2.0 / Fa
ptAns1X = T6 * ptAns1Y + T7
ptAns2X = T6 * ptAns2Y + T7
ptAns1X = ptAns1X + EllpCenX #
平移
ptAns1Y = ptAns1Y + EllpCenY #
平移
ptAns2X = ptAns2X + EllpCenX
ptAns2Y = ptAns2Y + EllpCenY
pttans0X = ptAns1X

def ellSlicesbyMile(xxin,yyin,x0,y0,x1,y1,x2,y2,angbeg,angend,npt):
xout=[]
yout=[]
pts=[]
npt,xout,yout,pts=ellipsemaker_XY(x0,y0,x1,y1,x2,y2,angbeg,angend,npt)
miles=[]
xcen,ycen,miles=Milelinexy_cen(xout,yout,1)
print('in ellSlicesbyMile ^^miles',miles)
xxonEll=[]
yyonEll=[]
xxonEll.append(xout[0]) # add the first point of ellipse
yyonEll.append(yout[0])
for i in range(len(xxin)):
nint,ptonEllipx,ptonEllipy,tAng=point_onEllipse_Angle(xxin[i],yyin[i],x0,y0,x1,y1,x2,y2,angbeg,angend,npt)
if nint==1:
xxonEll.append(ptonEllipx)
yyonEll.append(ptonEllipy)
xxonEll.append(xout[-1])# add the last point of ellipse
yyonEll.append(yout[-1])
milesAns=[]
milesAns.append(miles[0]) # add the first mile of ellipse
for i in range(len(xxonEll)):
yesorno,miletpt=MilesEllipse_givenXy(xxonEll[i],yyonEll[i],xout,yout)
if yesorno==1:
milesAns.append(miletpt)
milesAns.append(miles[-1]) # add the last mile of ellipse
print('in ellSlicesbyMile milesAns',milesAns)
xysegAll=[]
nbeg=0
for i in range(len(xxonEll)-1):
xyseg=[]
xyseg.append([xxonEll[i],yyonEll[i]]) #first point of segment
for j in range(len(xout)-1):
if miles[j]>=milesAns[i] and miles[j]>=milesAns[i+1]:
xyseg.append([xout[j],yout[j]])
xyseg.append([xxonEll[i+1],yyonEll[i+1]]) #last point of segment
xysegAll.append(xyseg)
return xxonEll,yyonEll,xysegAll
pttans0Y = ptAns1Y
pttans1X = ptAns2X
pttans1Y = ptAns2Y
Ellipse2Tans = 1
Ltans0 = math.sqrt((pttans0X - PtGivenX) ** 2 + (pttans0Y -
PtGivenY) ** 2)
Ltans1 = math.sqrt((pttans1X - PtGivenX) ** 2 + (pttans1Y -
PtGivenY) ** 2)
return pttans0X,pttans0Y,pttans1X,pttans1Y,Ltans0,Ltans1
<to be continued.>
|

